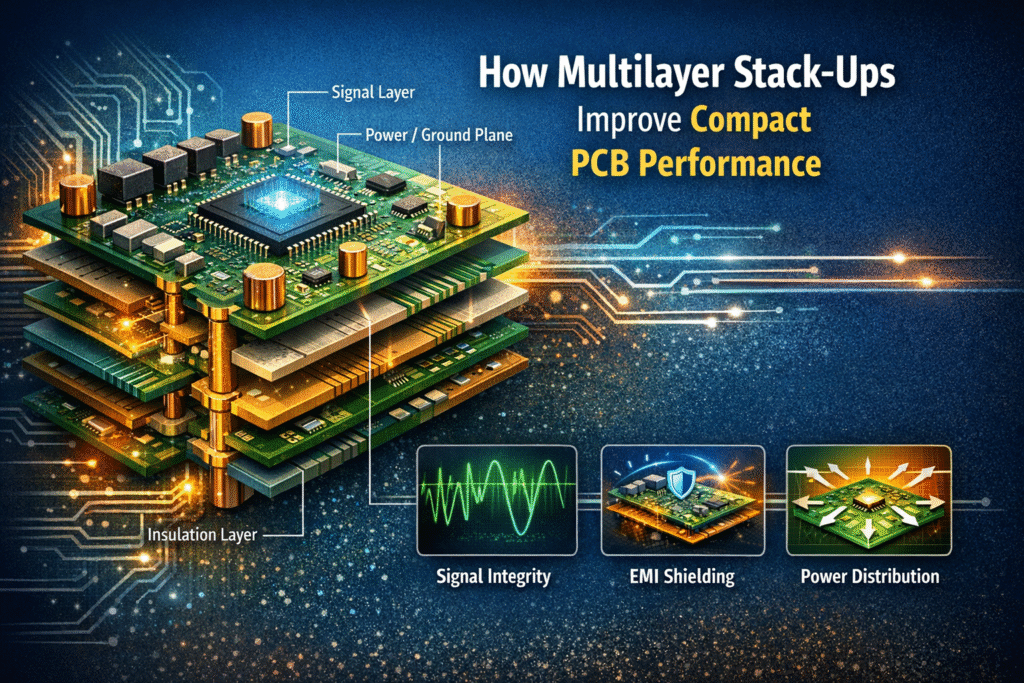
As electronic devices continue to shrink while delivering higher performance, designers are under constant pressure to fit more functionality into less space. This challenge has made compact printed circuit boards a standard requirement across many industries. Within this landscape, multilayer PCB stack-ups have become a crucial design strategy. When combined with thoughtful engineering and professional PCB Layout Services, multilayer designs significantly enhance performance, reliability, and manufacturability in space-constrained electronics.
Multilayer stack-ups are not just about adding more layers; they are about organizing electrical, power, and signal paths in a way that supports speed, stability, and long-term functionality. Understanding how these stack-ups improve compact PCB performance helps designers make informed decisions that align with current design standards and evolving technology demands.
Understanding Multilayer PCB Stack-Ups
A multilayer PCB consists of three or more conductive layers separated by insulating materials and bonded together into a single structure. Unlike single- or double-layer boards, multilayer designs allow signals, power, and ground planes to be distributed across dedicated layers. This layered approach becomes essential when board size is limited but circuit complexity is high.
Stack-up planning refers to the strategic arrangement of these layers. It determines where signal layers sit in relation to power and ground planes, how impedance is controlled, and how electromagnetic interference is minimized. In compact PCBs, every layer must serve a clear purpose to avoid unnecessary complexity while maximizing performance.
Why Compact PCB Designs Rely on Multilayer Structures
Compact PCB designs face several inherent challenges, including limited routing space, increased signal density, thermal buildup, and higher susceptibility to noise. Multilayer stack-ups address these challenges by offering greater control over electrical behavior within a confined footprint.
By distributing circuits vertically rather than horizontally, designers can route complex connections without overcrowding a single layer. This vertical expansion is one of the most effective ways to enhance board functionality without increasing physical dimensions.
Improved Signal Integrity in High-Density Layouts
One of the most significant performance benefits of multilayer stack-ups is improved signal integrity. As signal speeds increase, issues such as crosstalk, reflections, and impedance mismatch become more pronounced—especially in compact layouts.
Dedicated ground planes placed adjacent to signal layers provide a stable reference path, reducing loop areas and minimizing electromagnetic interference. Controlled impedance routing becomes easier when signal layers are sandwiched between reference planes. This structure ensures cleaner signal transmission, even in high-frequency or high-speed applications.
For compact boards where traces are closely packed, this level of control is essential to maintain consistent performance across all operating conditions.
Efficient Power Distribution and Voltage Stability
Power integrity is another critical factor in compact PCB performance. Multilayer stack-ups allow designers to dedicate entire layers to power and ground distribution, resulting in lower resistance and inductance compared to narrow power traces.
These planes act as low-impedance paths that stabilize voltage delivery across the board. This is particularly important in compact designs where multiple components draw power simultaneously and voltage fluctuations can cause malfunctions or reduced lifespan.
With proper stack-up planning, decoupling capacitors become more effective, and transient current demands are handled efficiently. This results in improved overall system reliability and predictable electrical behavior.
Thermal Management Advantages of Multilayer PCBs
As components become smaller and more powerful, heat dissipation becomes a growing concern. Compact PCBs have less surface area to release heat, making thermal management a priority.
Multilayer stack-ups support better heat distribution by spreading thermal energy across internal copper layers. Ground and power planes can act as heat spreaders, drawing heat away from critical components. Thermal vias further enhance this effect by transferring heat between layers.
This layered heat distribution helps maintain stable operating temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal stress, signal degradation, and premature component failure.
Enhanced Routing Flexibility Without Increasing Board Size
Routing density is a major limitation in compact PCB designs. Single or double-layer boards quickly become congested, leading to inefficient routing and potential design compromises.
Multilayer stack-ups provide additional routing channels that allow signals to be separated logically. Sensitive signals can be isolated from noisy ones, and high-speed traces can be routed on optimal layers. This flexibility leads to cleaner layouts and reduces the need for excessive vias or long trace paths.
Designers using structured stack-ups can maintain readability and manufacturability, even in highly complex circuits.
Reduced Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference is a common issue in compact electronics due to close component spacing and high signal density. Multilayer PCBs help mitigate EMI by incorporating continuous reference planes that shield signal layers.
Ground planes absorb and contain electromagnetic emissions, preventing them from radiating outward or interfering with nearby traces. Symmetrical stack-up designs also help balance electromagnetic fields, further reducing noise.
This is especially valuable in designs that must meet strict regulatory or performance standards without relying on external shielding.
Mechanical Stability and Long-Term Reliability
Beyond electrical benefits, multilayer stack-ups also improve mechanical strength. Additional layers increase board rigidity, reducing the likelihood of warping or cracking during assembly and operation.
This structural stability is important for compact PCBs, which often undergo thermal cycling, vibration, or mechanical stress. A well-balanced stack-up distributes stress evenly across the board, supporting long-term reliability in demanding environments.
Design Planning and Compact PCB Considerations
Effective multilayer stack-up design requires early planning and collaboration between electrical, mechanical, and manufacturing considerations. Designers must account for layer count, material selection, trace widths, and spacing rules to achieve optimal results.
At this stage, understanding broader compact PCB design principles is essential. Factors such as component placement, routing strategy, and manufacturing constraints play a critical role in determining whether a multilayer approach delivers its intended benefits.
A detailed discussion of these foundational aspects is explored in this guide on key considerations when designing compact PCBs, which fits naturally into the design process and supports better stack-up decisions:
By aligning stack-up planning with these broader considerations, designers can avoid rework and improve first-pass success.
Supporting Manufacturability in Compact Designs
Multilayer stack-ups also support design for manufacturability when planned correctly. Clear separation of layers, consistent trace rules, and standardized stack structures reduce fabrication complexity.
Manufacturers benefit from predictable layer arrangements and balanced copper distribution, which improves yield and reduces production risks. Compact boards designed with manufacturability in mind are more cost-effective over their lifecycle, even if the initial design effort is higher.
Adapting to Modern Design and SEO-Driven Engineering Content
As technology evolves, design knowledge must be documented clearly and accurately. From an information perspective, content related to multilayer stack-ups must reflect real-world engineering practices, current standards, and user intent.
High-quality technical content today prioritizes clarity, originality, and practical insight over keyword repetition. When discussing topics like PCB Layout Services, the focus should remain on how design choices impact performance rather than promotional messaging.
This approach aligns with modern content quality expectations, ensuring information remains useful, trustworthy, and relevant.
The Role of Expertise in Stack-Up Optimization
While design tools continue to advance, multilayer stack-up optimization remains a skill-driven process. Experience helps designers balance performance, cost, and manufacturability without overengineering the solution.
Access to knowledgeable layout expertise ensures that each layer contributes meaningfully to performance. From impedance control to thermal planning, expert input reduces trial-and-error and accelerates development timelines.
Conclusion: Why Multilayer Stack-Ups Matter in Compact PCBs
Multilayer stack-ups play a critical role in improving compact PCB performance by enhancing signal integrity, stabilizing power delivery, managing heat, and reducing electromagnetic interference. They allow designers to overcome space limitations without sacrificing reliability or functionality.
When paired with careful planning, sound engineering principles, and well-executed PCB Layout Services, multilayer designs enable compact electronics to meet modern performance expectations. As devices continue to shrink and complexity grows, structured stack-up strategies will remain a cornerstone of successful PCB design.
By focusing on clarity, balance, and real-world application, multilayer stack-ups help bridge the gap between compact form factors and high-performance electronics—making them essential in today’s evolving design landscape.