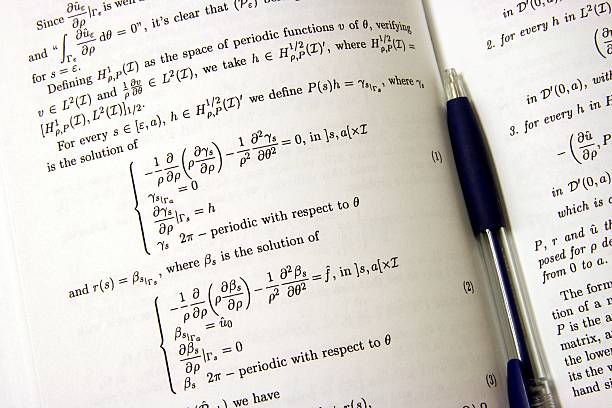Introduction to MATLAB in Aerospace Engineering
MATLAB is a versatile tool widely used in aerospace engineering to perform complex computations, simulations, and data analyses. Aerospace engineering relies heavily on mathematical modeling, and MATLAB provides a platform to execute these models efficiently. From analyzing flight dynamics to simulating aerodynamics, MATLAB allows engineers to transform theoretical concepts into practical, testable results.
The aerospace industry demands precision, speed, and reliability, and MATLAB’s extensive library of functions and toolboxes is tailored to meet these needs. Engineers can quickly solve equations, design control systems, and visualize data, which accelerates the development of innovative aerospace solutions.
Key Applications of MATLAB in Aerospace Engineering
1. Flight Dynamics and Control Systems
Flight dynamics is a critical aspect of aerospace engineering. Engineers need to analyze how aircraft respond to control inputs and environmental conditions. MATLAB facilitates this by allowing the simulation of aircraft motion using mathematical models. Control system design, including stability analysis and autopilot development, is simplified with MATLAB’s Control System Toolbox.
Engineers can design feedback loops, test controllers in simulated environments, and optimize system parameters to ensure safe and efficient aircraft operations. The visualization features of MATLAB further help in presenting simulation results in an understandable manner.
2. Aerodynamic Analysis and Simulation
Aerodynamics plays a central role in aerospace engineering, influencing everything from aircraft performance to fuel efficiency. MATLAB enables engineers to perform computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, analyze airflow patterns, and optimize wing designs. By integrating MATLAB with Simulink, engineers can model complex aerodynamic systems and evaluate their performance under different conditions.
This capability ensures that engineers can predict potential issues early in the design process, saving time and resources. Accurate aerodynamic analysis leads to safer and more fuel-efficient aircraft.
3. Satellite and Spacecraft Modeling
MATLAB is extensively used in modeling satellite trajectories and spacecraft dynamics. Aerospace engineers utilize MATLAB to simulate orbital mechanics, mission planning, and satellite attitude control systems. The Aerospace Toolbox in MATLAB offers specialized functions for analyzing orbital paths, calculating orbital parameters, and simulating satellite maneuvers.
Simulation results help engineers make informed decisions about propulsion, fuel usage, and mission timing. This contributes to successful satellite deployment and mission efficiency.
4. Structural Analysis and Material Testing
The structural integrity of aerospace components is crucial for safety. MATLAB allows engineers to perform stress analysis, vibration testing, and fatigue simulations on aircraft parts. By combining MATLAB with finite element analysis (FEA) tools, engineers can predict the behavior of materials under different loads and conditions.
This predictive capability helps prevent structural failures, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of aerospace vehicles. MATLAB’s data visualization features make it easier to interpret simulation results and make engineering decisions confidently.
Enhancing MATLAB Efficiency with Best Practices
Writing Optimized Code
Efficient MATLAB coding is essential for managing large datasets and performing high-complexity simulations. Aerospace engineers should focus on vectorization, preallocating arrays, and minimizing the use of loops to improve execution speed. Optimized code ensures that simulations run faster without compromising accuracy.
Modular Design and Documentation
Organizing code into modular functions enhances readability, reusability, and maintainability. Aerospace projects often involve multiple engineers working on different aspects of the system. Clear documentation and well-structured code improve collaboration and reduce errors during project execution.
Integration with External Tools
MATLAB can be integrated with other software tools commonly used in aerospace engineering, including CAD software, CFD solvers, and real-time simulation platforms. This integration allows engineers to streamline workflows and ensure consistent results across various stages of aircraft or spacecraft development.
Data Visualization and Reporting
MATLAB excels in creating high-quality visualizations, which are critical in aerospace engineering. Engineers can plot flight paths, aerodynamic forces, structural stresses, and other key metrics. Clear visualizations help communicate complex data to stakeholders, including non-technical team members, enhancing decision-making processes.
MATLAB for Research and Advanced Aerospace Projects
MATLAB is not limited to industrial applications; it is also essential for aerospace research and academic projects. Students and researchers use MATLAB for modeling new propulsion systems, analyzing flight test data, and developing innovative control algorithms. The ability to simulate scenarios before real-world testing reduces costs and mitigates risks.
For researchers looking to combine financial modeling with aerospace applications, seeking best derivatives pricing options writing help can also provide insights into integrating complex numerical methods in simulations. This cross-disciplinary approach strengthens analytical skills and broadens engineering capabilities.
Challenges in MATLAB Writing for Aerospace Applications
Despite its advantages, using MATLAB in aerospace engineering presents certain challenges. Complex simulations can be computationally intensive, requiring high-performance computing resources. Additionally, aerospace engineers must stay updated with evolving MATLAB toolboxes and best practices to leverage the software effectively.
Debugging and verifying simulation results are critical steps, as errors in modeling can lead to inaccurate conclusions. Proper validation against experimental data is necessary to ensure reliability. Continuous learning and collaboration with peers help overcome these challenges and maintain high standards of accuracy.
Conclusion
MATLAB writing has become indispensable in aerospace engineering, offering tools for flight dynamics, control systems, aerodynamics, satellite modeling, and structural analysis. Efficient coding, modular design, and integration with external tools enhance productivity and simulation accuracy.
By mastering MATLAB, aerospace engineers can optimize designs, reduce costs, and improve safety across a wide range of projects. Its combination of computational power, visualization capabilities, and versatility ensures that MATLAB remains a cornerstone of both academic research and industrial aerospace applications.
As aerospace engineering continues to evolve, the ability to write effective MATLAB code will remain a critical skill, enabling engineers to meet the demands of innovation and precision in one of the most challenging fields of engineering.