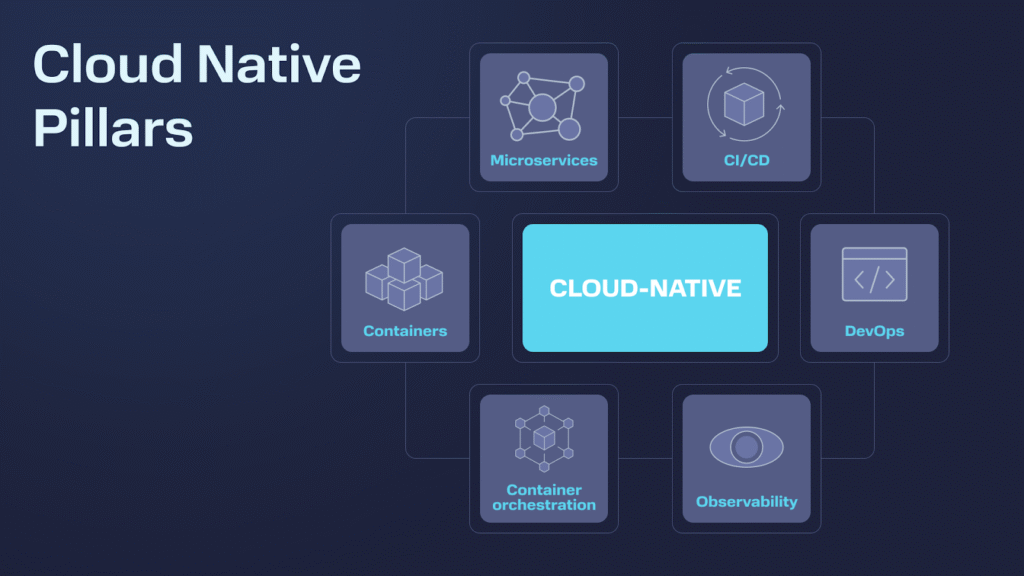
Cloud-native applications have transformed the way organizations design, develop, and deploy software. Instead of relying on monolithic architectures and fixed infrastructure, modern applications are built using microservices, containers, continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD), and dynamic cloud platforms. These applications are designed to scale automatically, recover from failures quickly, and adapt to changing business needs.
Among modern programming languages, Java remains one of the most powerful choices for cloud-native development. Its mature ecosystem, platform independence, and strong framework support make it highly suitable for distributed environments. Professionals looking to master these technologies often explore structured learning options such as Cloud Computing Courses in Chennai to gain practical exposure to real-world cloud deployments.
Platform Independence and Portability
One of Java’s greatest strengths is its platform independence. Java programs may operate on any system that supports the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) according to the “Write Once, Run Anywhere” philosophy. This feature is particularly valuable in cloud environments, where applications may be deployed across various operating systems and infrastructure providers.
Cloud-native applications often move between development, testing, and production environments. Java’s portability ensures consistent behavior across these stages. Whether deployed on public clouds, private clouds, or hybrid environments, Java applications maintain compatibility and stability.
Strong Microservices Support
Cloud-native architecture commonly relies on microservices small, independent services that communicate through APIs. Java offers excellent support for microservices development through powerful frameworks such as:
- Spring Boot
- Jakarta EE
- Micronaut
- Quarkus
Spring Boot, in particular, simplifies microservices creation by offering auto-configuration, embedded servers, and production-ready features. Developers can build lightweight, scalable services quickly without complex setup.
These technologies are frequently covered in professional upskilling programs and executive technology modules offered in collaboration with a leading B School in Chennai, where digital transformation and scalable architecture are key learning areas.
Containerization and Kubernetes Compatibility
Containers are a core component of cloud-native systems. Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes allow applications to run consistently across environments while providing scalability and orchestration.
Java works seamlessly with container platforms. Modern Java frameworks are designed to be container-friendly, reducing memory footprint and startup time. Additionally, tools like Jib allow developers to build container images directly from Java projects without requiring a Dockerfile.
When deployed in Kubernetes clusters, Java applications can:
- Automatically scale based on demand
- Restart failed services
- Balance traffic efficiently
- Support rolling updates with minimal downtime
This integration makes Java a reliable choice for dynamic cloud deployments.
Reactive and Scalable Architectures
Cloud-native applications must handle high traffic loads and unpredictable usage patterns. Java supports reactive programming models that enable asynchronous, non-blocking operations.
Frameworks such as Spring WebFlux and Vert.x allow developers to build reactive systems that:
- Handle thousands of concurrent requests
- Improve resource utilization
- Enhance responsiveness
Reactive programming ensures that applications remain scalable and resilient under heavy workloads, a key requirement for cloud-native systems.
DevOps and CI/CD Integration
Cloud-native development heavily depends on DevOps practices and continuous integration/continuous deployment pipelines. Java integrates smoothly with CI/CD tools such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and Azure DevOps.
Maven and Gradle, Java’s popular build automation tools, support dependency management, testing, packaging, and deployment. These tools make it easier to automate:
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- Static code analysis
- Container image creation
- Deployment to cloud platforms
This strong DevOps compatibility ensures faster delivery cycles and improved reliability.
Cloud Platform Integration
Java offers extensive support for major cloud providers, including:
- AWS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
Each of these platforms provides SDKs and libraries specifically for Java. Developers can easily integrate services such as:
- Cloud storage
- Managed databases
- Messaging systems
- Serverless functions
- Identity and access management
Spring Cloud further enhances integration by providing tools for service discovery, configuration management, distributed tracing, and circuit breakers. These features are essential for managing microservices in distributed cloud environments.
Built-In Security Features
Security is essential in distributed cloud systems. Java includes strong security mechanisms such as bytecode verification, cryptography APIs, and secure class loading.
Frameworks like Spring Security enable authentication, authorization, OAuth2 integration, and JWT-based protection. Secure coding practices are often reinforced in structured training programs and workshops conducted by a recognized Coaching Institute in Chennai, preparing professionals to build resilient applications.
Observability and Monitoring
Cloud-native systems require continuous monitoring and observability to maintain performance and detect issues quickly. Java supports monitoring tools such as:
- Micrometer
- Prometheus
- Grafana
- OpenTelemetry
Spring Boot Actuator provides built-in endpoints for health checks, metrics, and application monitoring. These features allow teams to track system health, analyze performance trends, and troubleshoot problems efficiently.
Observability ensures that Java applications remain reliable and responsive in production environments.
Performance Optimization with Modern JVM Enhancements
Over the years, the JVM has significantly improved in performance and efficiency. Modern versions of Java provide:
- Improved garbage collection algorithms
- Better memory management
- Faster startup times
- Lower latency
Projects like GraalVM further enhance performance by enabling native image compilation. This reduces startup time and memory usage, making Java even more suitable for serverless and containerized environments.
These optimizations address earlier concerns about Java being resource-heavy, positioning it as a competitive option for modern cloud workloads.
Large Community and Ecosystem Support
One of the biggest developer communities in the world is found in Java. This mature ecosystem ensures:
- Continuous innovation
- Regular security updates
- Extensive documentation
- Community-driven improvements
The availability of libraries, frameworks, and third-party integrations accelerates development. Enterprises benefit from long-term support (LTS) versions, ensuring stability and reliability for mission-critical cloud-native systems.
A strong community also means faster troubleshooting and access to shared knowledge, reducing development time and operational risks.
Backward Compatibility and Enterprise Reliability
Many organizations still rely on legacy systems. Java’s backward compatibility allows businesses to modernize gradually without rewriting entire systems.
Cloud-native transformation often involves migrating existing monolithic applications into microservices. Java supports this process by allowing incremental refactoring and integration with modern cloud tools.
This enterprise-grade reliability makes Java a practical choice for both startups and large organizations undergoing digital transformation.
Cloud-native applications demand scalability, resilience, flexibility, and rapid deployment. Java successfully meets these requirements through its platform independence, strong microservices frameworks, container compatibility, reactive programming support, and seamless cloud integration.
With modern enhancements like GraalVM, improved JVM performance, and cloud-optimized frameworks such as Spring Boot and Quarkus, Java has evolved to align perfectly with cloud-native principles. Its robust ecosystem, security features, and DevOps compatibility further strengthen its position as a leading technology for cloud development.
In an era where agility and scalability define success, Java continues to prove that it is not just a legacy language but a powerful foundation for building modern, cloud-native applications.